Lightweight Verifiable Computation Primitives
Verifiable computation in most systems today is done through the use of message authentication codes and zero knowledge proofs. In quantum resistant settings, however, achieving verifiability becomes significantly more challenging. Many post quantum constructions, especially those based on lattices, already incur large keys, high memory usage, and expensive polynomial arithmetic. Adding generic proof systems on top of these operations can introduce prohibitive overhead. The difficulty is even greater in homomorphic encryption systems, where noise growth, ciphertext expansion, and costly evaluation steps already push performance limits. Verifying the correctness of homomorphic computations with traditional post quantum proof techniques can therefore become impractical for real world or latency sensitive applications. This is why lightweight application specific primitives are essential. By tailoring verification mechanisms to the exact structure and behavior of the homomorphic computation, these primitives minimize overhead, reduce proof complexity, and provide practical integrity guarantees while maintaining quantum resistant security.
The technical contributions of this work are:
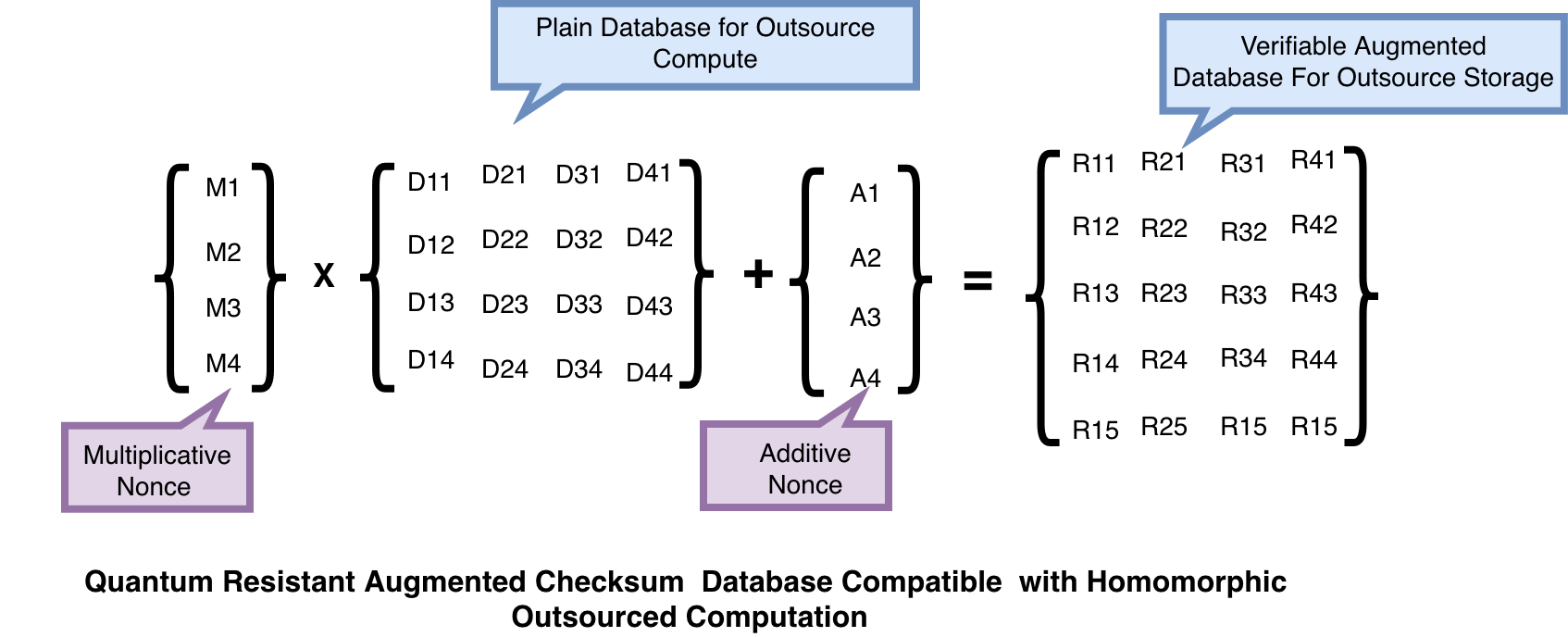
- We analyze a range of homomorphic encryption applications and identify the structural constraints that make generic verification prohibitively expensive. Based on this analysis, we design lightweight verification mechanisms that align with the algebraic behavior of homomorphic operations, including augmented checksums and structured redundancy tests that preserve correctness with minimal overhead.
- We develop quantum resistant integrity mechanisms that operate efficiently within lattice based cryptographic settings. These include collision resistant hash based verification procedures and application specific constructions that avoid the high cost of generic post quantum zero knowledge proofs while maintaining soundness under standard post quantum assumptions.
- Beyond homomorphic encryption, we introduce verification strategies that apply broadly to outsourced computation environments. These techniques emphasize simplicity, low communication cost, and compatibility with diverse cryptographic systems, providing a practical foundation for verifiable computation in resource constrained or latency sensitive applications.
Background
Verifiable computing is a cryptographic approach that allows a client to offload a computation to an untrusted server while still being able to efficiently check that the returned result is correct. Instead of repeating the entire computation, the client verifies a small proof that certifies the correctness of the output. This is important in modern systems where heavy workloads are delegated to cloud services, distributed networks, or specialized hardware. Verifiable computing strengthens trust, ensures integrity even in adversarial environments, reduces the cost for clients, and underpins practical techniques such as zero knowledge proofs, SNARKs, and integrity checked homomorphic computations.Capabilities
Our system provides a suite of custom designed verification mechanisms that are tailored to the structure of homomorphic operations and post quantum arithmetic. These primitives include augmented checksums, structured redundancy encodings, and hash based integrity checks that introduce negligible computational and communication overhead. Each primitive is built to operate natively within lattice based cryptographic systems, ensuring compatibility with homomorphic evaluation pipelines while maintaining strong post quantum security guarantees. This enables practical integrity verification without relying on expensive universal proof systems.
We also provide optimized zero knowledge proof components that leverage parallelism, vectorized polynomial operations, and hardware acceleration paths when available. These ZKP primitives are streamlined for post quantum workloads and are designed to interoperate efficiently with both homomorphic schemes and standalone verification contexts. By reducing proof size, improving prover throughput, and exploiting hardware features such as SIMD units, GPUs, and specialized polynomial arithmetic engines, our approach provides high performance verification support suitable for large scale and latency sensitive applications.